 Updated March 2023: using K3s 1.25 and Ubuntu 22.04
Updated March 2023: using K3s 1.25 and Ubuntu 22.04
K3s is a lightweight Kubernetes deployment by Rancher that is fully compliant, yet also compact enough to run on development boxes and edge devices.
In this article, I will show you how to deploy a three-node K3s cluster on Ubuntu nodes that are created using Terraform and a local KVM libvirt provider.
This article focuses on the minimal manual steps for a K3s cluster. I have an automated example using Ansible in another article.
Creating node VMs
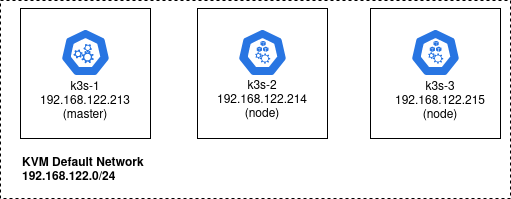
We will deploy this K3s cluster on three independent guests running Ubuntu.
These Ubuntu VMs could actually be created using any hypervisor or hyperscaler, but for this article we will use Terraform and the local KVM libvirt provider to create guests named: k3s-1, k3s-2, k3s-3. We will place them on the standard KVM default network, 192.168.122.0/24.
Install Terraform, its libvirt provider, and KVM as described in a previous article. Then use my github project to create the three Ubuntu guest OS.
# required packages sudo apt install make git curl -y # github project with terraform to create guest OS git clone https://github.com/fabianlee/k3s-cluster-kvm.git cd k3s-cluster-kvm # run terraform init and apply cd tf-libvirt # make ssh keypair for login as 'ubuntu' ssh-keygen -t rsa -b 4096 -f id_rsa -C tf-libvirt -N "" -q # initialize terraform and its plugins terraform init # do creation terraform apply -auto-approve
The KVM guests can now be listed using virsh. I have embedded the IP address in the libvirt domain name to make the address obvious.
# should show three running k3s VMs $ virsh list Id Name State -------------------------------------------- ... 10 k3s-1-192.168.122.213 running 11 k3s-2-192.168.122.214 running 12 k3s-1-192.168.122.215 running
cloud-init has been used to give the ‘ubuntu’ user an ssh keypair for login, which allows us to validate the login for each host using the command below.
# accept key as known_hosts for octet in $(seq 213 215); do ssh-keyscan -H 192.168.122.$octet >> ~/.ssh/known_hosts; done # test ssh into remote host for octet in $(seq 213 215); do ssh -i id_rsa ubuntu@192.168.122.$octet "hostname -f; uptime"; done
Updating hosts files for K3s cluster
To allow all the VMs participating in the K3s cluster to see each other, add entries to /etc/hosts. Do this either manually like below:
# login to each host manually # ssh -i id_rsa ubuntu@192.168.122.[213-215] # add these entries to each /etc/hosts k3s-1 192.168.122.213 k3s-2 192.168.122.214 k3s-3 192.168.122.215
Or you can use this single command.
for octet in $(seq 213 215); do ssh -i id_rsa ubuntu@192.168.122.$octet 'echo -e "k3s-1 192.168.122.213\nk3s-2 192.168.122.214\nk3s-3 192.168.122.215" | sudo tee -a /etc/hosts'; done
Install master K3s node
Login manually to the K3s master node (.213) and run these commands.
# login to master $ ssh -i id_rsa ubuntu@192.168.122.213 # install $ sudo curl -sfL https://get.k3s.io | sh - [INFO] Finding release for channel stable [INFO] Using v1.25.7+k3s1 as release [INFO] Downloading hash https://github.com/k3s-io/k3s/releases/download/v1.25.7+k3s1/sha256sum-amd64.txt [INFO] Downloading binary https://github.com/k3s-io/k3s/releases/download/v1.25.7+k3s1/k3s [INFO] Verifying binary download [INFO] Installing k3s to /usr/local/bin/k3s [INFO] Skipping installation of SELinux RPM [INFO] Creating /usr/local/bin/kubectl symlink to k3s [INFO] Creating /usr/local/bin/crictl symlink to k3s [INFO] Creating /usr/local/bin/ctr symlink to k3s [INFO] Creating killall script /usr/local/bin/k3s-killall.sh [INFO] Creating uninstall script /usr/local/bin/k3s-uninstall.sh [INFO] env: Creating environment file /etc/systemd/system/k3s.service.env [INFO] systemd: Creating service file /etc/systemd/system/k3s.service [INFO] systemd: Enabling k3s unit Created symlink /etc/systemd/system/multi-user.target.wants/k3s.service → /etc/systemd/system/k3s.service. [INFO] systemd: Starting k3s
And then do a validation to ensure the service is started and kubectl reports back a single master node.
# validate service, status should say 'active (running)'
$ sudo systemctl status k3s --no-pager | head -n5
k3s.service - Lightweight Kubernetes
Loaded: loaded (/etc/systemd/system/k3s.service; enabled; vendor preset: enabled)
Active: active (running) since Sun 2021-09-12 20:39:32 UTC; 5min ago
Docs: https://k3s.io
Process: 3050 ExecStartPre=/bin/sh -xc ! /usr/bin/systemctl is-enabled --quiet nm-cloud-setup.service (code=exited, status=0/SUCCESS)
# validate that kubectl returns single master
$ sudo kubectl get nodes -o wide
NAME STATUS ROLES AGE VERSION INTERNAL-IP EXTERNAL-IP OS-IMAGE KERNEL-VERSION CONTAINER-RUNTIME
k3s-1 Ready control-plane,master 18s v1.25.7+k3s1 192.168.122.213 Ubuntu 22.04.2 LTS 5.15.0-69-generic containerd://1.6.15-k3s1
The master node has a file “/var/lib/rancher/k3s/server/node-token” which we will use in the next section to add nodes to the cluster.
Join K3s nodes to the cluster
In order to add K3s nodes to the master, we need to use the key found on the master at “/var/lib/rancher/k3s/server/node-token”. So let’s capture that value.
k3s_master=192.168.122.213 # grab node token from master node_token=$(ssh -i id_rsa ubuntu@$k3s_master "sudo cat /var/lib/rancher/k3s/server/node-token") echo "node_token from master is $node_token"
To create a cluster run the get.k3s.io script just like the master, but this time add parameters for the master node IP and node token.
# install on k3s-2, join cluster
$ ssh -i id_rsa ubuntu@192.168.122.214 "sudo curl -sfL http://get.k3s.io | K3S_URL=https://${k3s_master}:6443 K3S_TOKEN=${node_token} sh -"
[INFO] Finding release for channel stable
[INFO] Using v1.25.7+k3s1 as release
[INFO] Downloading hash https://github.com/k3s-io/k3s/releases/download/v1.25.7+k3s1/sha256sum-amd64.txt
[INFO] Downloading binary https://github.com/k3s-io/k3s/releases/download/v1.25.7+k3s1/k3s
[INFO] Verifying binary download
[INFO] Installing k3s to /usr/local/bin/k3s
[INFO] Skipping installation of SELinux RPM
[INFO] Creating /usr/local/bin/kubectl symlink to k3s
[INFO] Creating /usr/local/bin/crictl symlink to k3s
[INFO] Creating /usr/local/bin/ctr symlink to k3s
[INFO] Creating killall script /usr/local/bin/k3s-killall.sh
[INFO] Creating uninstall script /usr/local/bin/k3s-agent-uninstall.sh
[INFO] env: Creating environment file /etc/systemd/system/k3s-agent.service.env
[INFO] systemd: Creating service file /etc/systemd/system/k3s-agent.service
[INFO] systemd: Enabling k3s-agent unit
Created symlink /etc/systemd/system/multi-user.target.wants/k3s-agent.service → /etc/systemd/system/k3s-agent.service.
[INFO] systemd: Starting k3s-agent
In the same way, join the k3s-3 node.
# install on k3s-3, join cluster
$ ssh -i id_rsa ubuntu@192.168.122.215 "sudo curl -sfL http://get.k3s.io | K3S_URL=https://${k3s_master}:6443 K3S_TOKEN=${node_token} sh -"
Validate Kubernetes Cluster
A call to kubectl should now show all 3 nodes participating in the Kubernetes cluster.
$ ssh -i id_rsa ubuntu@192.168.122.213 "sudo kubectl get nodes" NAME STATUS ROLES AGE VERSION k3s-1 Ready control-plane,master 8m21s v1.25.7+k3s1 k3s-2 Ready 71s v1.25.7+k3s1 k3s-3 NotReady 3s v1.25.7+k3s
Validate app deployment to cluster
As a quick test of the Kubernetes cluster, create a test deployment of the whoami app which is exposed using the default K3s Traefik ingress.
# copy deployment manifest to master
scp -i id_rsa whoami_traefik_example.yml ubuntu@192.168.122.213:.
# login to master
ssh -i id_rsa ubuntu@192.168.122.213
# apply manifest
$ sudo kubectl apply -f whoami_traefik_example.yml
deployment.apps/whoami-ds created
service/whoami-service created
ingressroute.traefik.containo.us/whoami-ingressroute created
# exposed services should now have 'whoami-service'
$ sudo kubectl get services
NAME TYPE CLUSTER-IP EXTERNAL-IP PORT(S) AGE
kubernetes ClusterIP 10.43.0.1 443/TCP 49m
whoami-service ClusterIP 10.43.210.80 80/TCP 40s
# put ClusterIP of whoami service into variable
cluster_ip=$(sudo kubectl get service/whoami-service -o=jsonpath="{.spec.clusterIP}")
# request to service
$ curl http://$cluster_ip/whoami
Hostname: whoami-ds-78447d957f-jnfrw
IP: 127.0.0.1
IP: ::1
IP: 10.42.1.3
IP: fe80::18:13ff:febc:c0fb
RemoteAddr: 10.42.0.0:18326
GET /whoami HTTP/1.1
Host: 10.43.210.80
User-Agent: curl/7.68.0
Accept: */*
# also exposed by Traefik
$ sudo kubectl get service traefik -n kube-system
NAME TYPE CLUSTER-IP EXTERNAL-IP PORT(S) AGE
traefik LoadBalancer 10.43.214.196 192.168.122.213,192.168.122.214,192.168.122.215 80:30180/TCP,443:31528/TCP 59m
# available here from master node
$ curl http://localhost/whoami
$ curl http://k3s-1.local/whoami
# leave ssh session
exit
And Traefik also exposes this service externally.
# available also outside cluster $ curl http://192.168.122.213/whoami Hostname: whoami-ds-78447d957f-jnfrw IP: 127.0.0.1 IP: ::1 IP: 10.42.1.3 IP: fe80::18:13ff:febc:c0fb RemoteAddr: 10.42.0.8:35890 GET /whoami HTTP/1.1 Host: 192.168.122.213 User-Agent: curl/7.68.0 Accept: */* Accept-Encoding: gzip X-Forwarded-For: 10.42.0.1 X-Forwarded-Host: 192.168.122.213 X-Forwarded-Port: 80 X-Forwarded-Proto: http X-Forwarded-Server: traefik-97b44b794-k6bbx X-Real-Ip: 10.42.0.1 # available at each cluster node $ curl http://192.168.122.214/whoami $ curl http://192.168.122.215/whoami
REFERENCES
k3s installation official docs
computingforgeeks, installing k3s on ubuntu
liquidweb.com, installing k3s on ubuntu
niveditacoder, installing k3s on ubuntu
osradar, installing k3s on ubuntu20
github collabnix, installing k3s on ubuntu18
ivankrizsan.se, traefik ingress example on k3s
longhorn docs, distributed filesystem
dmacvicar, terraform local libvirt provider
Loic Fache, whoami example deployment on traefik
metallb, k3s klipper must be disabled if you want to use MetalLB
rancher, k3s without traefik and with nginx ingress
suse, k3s without traefik and with nginx ingress
unixorn, k3s without traefik on ARM
mpolednik, k3s on ARM with nginx and metalLB
kubernetes, nginx ingress bare metal with NodePort (used by k3s)
NOTES
view traefik dashboard
# http://127.0.0.1:9000/dashboard kubectl port-forward -n kube-system pod/traefik-97b44b794-4mpx5 9000:9000
k3s config.toml for configuration of containerd
sudo vi /var/lib/rancher/k3s/agent/etc/containerd/config.toml