 Updated Aug 2023: tested on Ubuntu 22 with QEMU 6.2.0/libvirt 8.0.0 and with Minikube v1.31.2
Updated Aug 2023: tested on Ubuntu 22 with QEMU 6.2.0/libvirt 8.0.0 and with Minikube v1.31.2
Minikube is a tool that runs a full Kubernetes stack on a host, making it ideal for local development and experimentation. We are taking it one step further by placing Minikube into a virtual machine run by the KVM virtualization engine, which will allow us to isolate multiple versions and instances.
In this article we’ll be going through installation and validation of a Minikube installation on Ubuntu using KVM as the hypervisor.
Prerequisite, install KVM
Go through the detailed instructions in my article here about installing KVM on Ubuntu.
Install kubectl
kubectl is the command line tool used to deploy and manage applications.
curl -Lo kubectl https://storage.googleapis.com/kubernetes-release/release/$(curl -s https://storage.googleapis.com/kubernetes-release/release/stable.txt)/bin/linux/amd64/kubectl && chmod +x kubectl && sudo mv kubectl /usr/bin/.
You can verify the version using:
# check path and version which kubectl kubectl version
Make sure you are using at least version 1.10, use of 1.6 will result in errors during deployment of the test application later.
Install minikube
Now download and put the latest minikube binary into /usr/local/bin
curl -Lo minikube https://storage.googleapis.com/minikube/releases/latest/minikube-linux-amd64 && chmod +x minikube && sudo mv minikube /usr/local/bin/ # check version minikube version
Install kvm2 drivers
Minikube leverages Docker Machine to manage the Kubernetes VM so that it benefits from the driver plugin architecture of Docker Machine. This requires that we install the KVM2 driver maintained by Minikube team.
# make sure official dependencies are already installed
sudo apt install libvirt-clients libvirt-daemon-system qemu-kvm
# install kvm2 driver
curl -LO https://storage.googleapis.com/minikube/releases/latest/docker-machine-driver-kvm2 && sudo install docker-machine-driver-kvm2 /usr/local/bin/
Start minikube
minikube start --vm-driver kvm2
This will begin with the minikube ISO being downloaded (~180Mb) and then will create the VM in VirtualBox named “minikube”.
KVM ‘virt-manager’ will now show the minikube VM.
And from the console, kubectl returns the service list from the fresh deployment.
$ minikube service list |-------------|------------|--------------| | NAMESPACE | NAME | URL | |-------------|------------|--------------| | default | kubernetes | No node port | | kube-system | kube-dns | No node port | |-------------|------------|--------------|
Validate Kubernetes connection
Use the ‘cluster-info’ command to validate that kubectl is able to connect to the minikube VM.
$ kubectl cluster-info Kubernetes master is running at https://192.168.39.104:8443 KubeDNS is running at https://192.168.39.104:8443/api/v1/proxy/namespaces/kube-system/services/kube-dns
Minikube creates a new KVM virtual bridge which will be on the 192.168.39.1/24 network (as opposed to the KVM default virtual bridge virbr0, which uses 192.168.122.1/24). View all the virtual bridges of your Ubuntu host using:
ip a | grep virbr
View a list of the available Kubernetes nodes.
$ kubectl get nodes NAME STATUS ROLES AGE VERSION minikube Ready control-plane 75s v1.27.4
And if you list the pods in all the namespaces, you will see the internal services supporting your Kubernetes installation.
$ kubectl get pods --all-namespaces NAMESPACE NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE kube-system coredns-5d78c9869d-hj5bn 1/1 Running 0 96s kube-system etcd-minikube 1/1 Running 0 107s kube-system kube-apiserver-minikube 1/1 Running 0 110s kube-system kube-controller-manager-minikube 1/1 Running 0 107s kube-system kube-proxy-mjzcc 1/1 Running 0 97s kube-system kube-scheduler-minikube 1/1 Running 0 107s kube-system storage-provisioner 1/1 Running 1 (65s ago) 105
Deploy test application
Now as a validation of the Kubernetes deployment, we will deploy a simple echo application.
$ kubectl run hello-minikube --image=registry.k8s.io/echoserver:1.10 --port=8080 deployment.apps "hello-minikube" created $ kubectl get pods NAME DESIRED CURRENT UP-TO-DATE AVAILABLE AGE hello-minikube 1 1 1 1 2m
After a few seconds, the ‘hello-minikube’ application will show status as ‘Running’ as shown below.
$ kubectl get pods NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE hello-minikube-6c47c66d8-k5dfj 1/1 Running 0 4m $ kubectl get services NAME TYPE CLUSTER-IP EXTERNAL-IP PORT(S) AGE kubernetes ClusterIP 10.96.0.1 <none> 443/TCP 36m
Now expose the service, and then minikube should be able see it and provide you a URL to the service.
$ kubectl expose pod hello-minikube --type=NodePort service/hello-minikube exposed $ kubectl get services NAME TYPE CLUSTER-IP EXTERNAL-IP PORT(S) AGE hello-minikube NodePort 10.106.191.125 8080:31421/TCP 10s kubernetes ClusterIP 10.96.0.1 443/TCP 11m $ minikube service list |-------------|----------------|-----------------------------| | NAMESPACE | NAME | URL | |-------------|----------------|-----------------------------| | default | hello-minikube | http://192.168.39.99:31421 | | default | kubernetes | No node port | | kube-system | kube-dns | No node port | |-------------|----------------|-----------------------------| $ minikube service hello-minikube --url http://192.168.39.99:31421
A curl to this URL adding a custom header and path:
curl -H "X-mytest: 123" $(minikube service hello-minikube --url)/path123
Will show these custom values in the response.
Hostname: hello-minikube Pod Information: -no pod information available- Server values: server_version=nginx: 1.13.3 - lua: 10008 Request Information: client_address=10.244.0.1 method=GET real path=/path123 query= request_version=1.1 request_scheme=http request_uri=http://192.168.39.99:8080/path123 Request Headers: accept=*/* host=192.168.39.99:31421 user-agent=curl/7.58.0 x-mytest=123 Request Body: -no body in request-
Kubernetes dashboard
If you want to view the Kubernetes web dashboard, you can start it and get the URL with the following command:
$ minikube dashboard --url Enabling dashboard ... Verifying dashboard health ... Launching proxy ... Verifying proxy health ... http://127.0.0.1:43743/api/v1/namespaces/kube-system/services/http:kubernetes-dashboard:/proxy/
Open the URL with a local browser and you should be able to see the “hello-minikube” deployment and pod as shown.
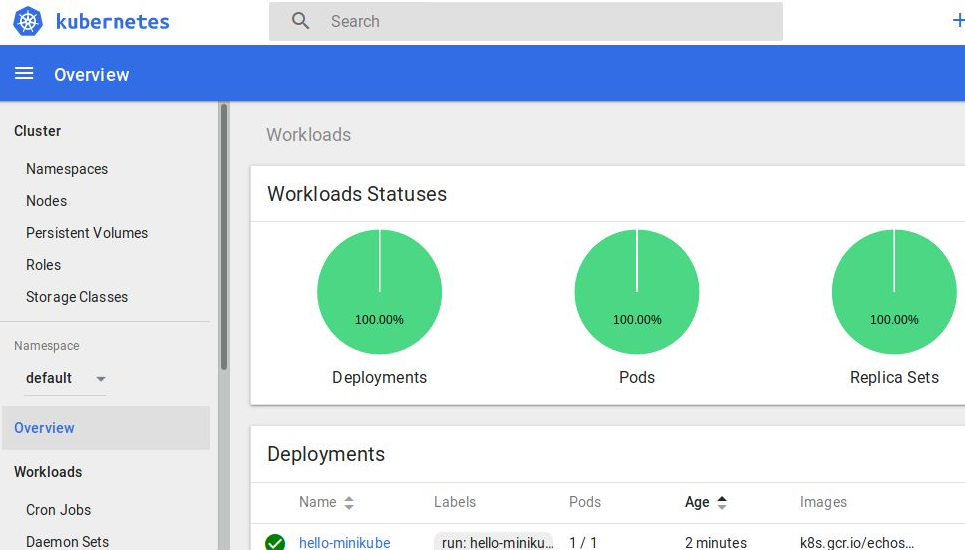
If you want to expose the dashboard using the proxy, read more here.
Stopping minikube
# stops the KVM VM minikube stop # start back up minikube start --vm-driver kvm2
The “hello-minikube” service will still be deployed after the restart.
Deleting service
# delete service kubectl get services kubectl delete service hello-minikube # delete pods kubectl get pods kubectl delete pod hello-minikube
REFERENCES
Kubernetes, installing Minikube
Official docs, Minikube on Linux
minikube, hello-minikube tutorial
KVM on bare metal for Ubuntu, fabianlee.org
KVM2 driver install before starting minikube
Getting off VirtualBox and moving to KVM for minikube
Quick summary of minikube commands
Problem that would be seen if minikube-net was not autostart, minikube mount
NOTES
ssh into minikube VM
minikube ssh # OR this works ssh -i ~/.minikube/machines/minikube/id_rsa docker@$(minikube ip) # find IP in logs as well minikube logs | grep -Po "current primary IP address \K[^ ]*"
minikube with more cpu/ram/disk
minikube start -h minikube start --cpus 4 --memory 8192 --disk-size 80g
Delete minikube VM from KVM
minikube delete
Show logs of service
minikube logs hello-minikube
make sure minikube-net KVM network is autostarting
virsh net-list --all
Same binary can start different versions of Kubernetes (per FAQ)
minikube start --kubernetes-version=v1.15.0