 As opposed to public GKE clusters which have their IP addresses exposed, private GKE clusters use private internal IP addresses that offer a level of security and segmentation that should always be preferred.
As opposed to public GKE clusters which have their IP addresses exposed, private GKE clusters use private internal IP addresses that offer a level of security and segmentation that should always be preferred.
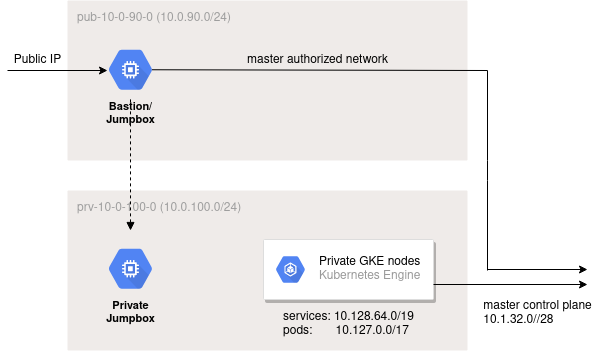
In this article, I will show you how to create a private GKE cluster with Terraform. The endpoint is private also for enhanced security, so must be managed from a public bastion/jumpbox.
Binary Prerequisites
Install the following binaries to prepare for the installation:
Google Cloud Prerequisites
Create a Google cloud project and subscribe to Anthos per the documentation.
- Login to the cloud console https://console.cloud.google.com with your Google Id
- Enable billing for the GCP project, Hamburger menu > Billing
- Enable the Anthos API, Hamburger menu > Anthos, click ‘Start Trial’
- Click ‘Enable’
From the console, initialize your login context to Google Cloud.
gcloud init gcloud auth login
Start build
Download my project from github, and start the build.
git clone https://github.com/fabianlee/gcp-gke-clusters-ingress.git cd gcp-gke-clusters-ingress # create unique project id ./generate_random_project_id.sh # select GKE version from REGULAR channel ./select_gke_version.sh # show build steps ./menu.sh
Continue build using menu actions
Follow the menu steps starting at the top and working your way down to create the project, networks, VMs, and finally the “privgke” action in order to create the private cluster described in this article.
project Create gcp project and enable services svcaccount Create service account for provisioning networks Create network, subnets, and firewall cloudnat Create Cloud NAT for public egress of private IP sshmetadata Load ssh key into project metadata vms Create VM instances in subnets enablessh Setup ssh config for bastions and ansible inventory ssh SSH into jumpbox ansibleping Test ansible connection to public and private vms ansibleplay Apply ansible playbook of minimal pkgs/utils for vms gke Create private GKE cluster w/public endpoint autopilot Create private Autopilot cluster w/public endpoint privgke Create private GKE cluster w/private endpoint privautopilot Create private Autopilot cluster w/private endpoint kubeconfigcopy Copy kubeconfig to jumpboxes
Run “kubeconfigcopy” in order to push the newly created kubeconfig to the jumpbox for your use in later steps.
Terraform module for private GKE cluster
The logic for the private GKE cluster in terraform is found in the main.tf of the gcp-gke-private-standard-cluster module.
This is where the google_container_cluster resource structure is defined.
Using kubectl to access the private cluster
This private GKE cluster purposely does not have a public endpoint enabled. To access the cluster you will need to be either:
- In the same subnet as the cluster nodes (10.0.100.0/24)
- Or in a specified master authorized network, which we have set as 10.0.90.0/24
This allows you to use kubectl from either the private jumpbox, or the public bastion/jumpbox in 10.0.90.0/24.
Run the “ssh” command and then select “vm-priv-10-0-100-0”. You will be forwarded through public bastion vm-pub-10-0-90-0 and into the private jumpbox.
The VM is preconfigured with the correct KUBECONFIG value, all you need to do is run “kubectl get nodes” to prove out the connection.
Destroy all GCP Objects
If you do not destroy all GCP objects, you will be charged. These menu items will assist in destroying, but you should do a manual check as well.
delgke Delete GKE public standard cluster delautopilot Delete GKE public Autopilot cluster delprivgke Delete GKE private standard cluster delprivautopilot Delete GKE private Autopilot cluster delvms Delete VM instances delnetworks Delete networks and Cloud NAT
REFERENCES
Peter Hrvola, 3 modes for GKE cluster exposure (public,public to specific CIDR, private)
Luca Prete, accessing GKE private clusters using IAP
davidc.net, CIDR block calculator with interactive divide/join
google github, private GKE cluster with terraform
ssorato, networking.gke.io/v1beta1.FrontendConfig: lb-http-to-https
alwaysupalwayson, GCP LB and Cloud Armor
google, pulling logs with query from gcloud
thegeekstuff.com, simulate XSS attack
codelabs google, Cloud Armor WAF rules
wdenniss.com, balloon pod with high priority to seed capacity of Autopilot
mikesparr, GCP LB with CloudArmor using gcloud example
johannes glen, GCP BackendConfig session affinity and NEG
theony.dev, terraform script for private gke custer
pbhadani.com, workload identity enabled GKE cluster
managedkube.com, example terraform for creating GKE cluster
kubernetes-engine-samples, whereami service
ssorato, example of private gke cluster terraform with lifecycle
google, workload identity test for pod access to google api