 Anthos Config Management (ACM) brings the power of GitOps to your GKE clusters.
Anthos Config Management (ACM) brings the power of GitOps to your GKE clusters.
Instead of needing to manually keep deployments current on a cluster or group of clusters, you can push changes to a git repository and the Config Sync component will periodically poll and attempt to reach the new state described by your git commit.
This allows you to administer a cluster from a central location, saving time and guaranteeing consistency. Additionally, you get the benefits of GitOps such as code review, audit, and rollback.
Prerequisites
To complete this article you need a standard GKE cluster, valid KUBECONFIG environment variable, and the gsutil and kubectl binary installed.
Then download the nomos utility, which is used to check the status of Config Sync.
# make sure auth is done via gcloud gcloud auth login # download nomos binary gsutil cp gs://config-management-release/released/latest/linux_amd64/nomos nomos # move to common location sudo mv nomos /usr/local/bin/. sudo chmod +x /usr/local/bin/nomos # validate nomos version
Prepare cluster
In order to participate in ACM, you need to register the cluster and enable workload identity which is the recommended method of authentication for the Config Sync component.
Setup variables
# check your current permissions, must respond 'yes' kubectl auth can-i '*' '*' --all-namespaces # get cluster list and region gcloud container clusters list # set variables project_id=$(gcloud config get-value project) cluster_name="<thecluster>" cluster_location="<theregion>" # set either 'region' or 'zone' location_flag="--region <theregion>" # get nodepool list gcloud container node-pools list --cluster $cluster_name $location_flag # set variable nodepool_name="<nodepool_name>"
Enable relevant Google API
# enable API services gcloud services enable anthos.googleapis.com container.googleapis.com gkeconnect.googleapis.com gkehub.googleapis.com cloudresourcemanager.googleapis.com iam.googleapis.com krmapihosting.googleapis.com # enable config management feature gcloud beta container hub config-management enable
Enable workload identity
You cannot register the GKE cluster if workload identity is not enabled on the cluster.
# needs to return <projectId>.svc.id.goog
gcloud container clusters describe $cluster_name --format="value(workloadIdentityConfig.workloadPool)" $location_flag
# IF workload identity is empty, then enable
# operation takes ~5-20 minutes
gcloud container clusters update $cluster_name $location_flag --workload-pool=${project_id}.svc.id.goog
# IF workload identity was empty, nodepool also needs update
# this does rolling rebuild of each node
# takes ~5min per node depending on max-surge and max-unavailable
gcloud container node-pools update $nodepool_name --cluster=$cluster_name $location_flag --workload-metadata=GKE_METADATA
Register cluster
With workload identity enabled, you can now register the cluster.
# list of clusters already registered gcloud container hub memberships list # register cluster KUBECONFIG=/tmp/kubeconfig-membership gcloud container hub memberships register $cluster_name --gke-cluster=$cluster_location/$cluster_name --enable-workload-identity
Egress for private GKE clusters
If you are on a private GKE cluster, then you need to either enable Cloud NAT to enable egress or enable Private Google Access as described in the official documentation.
public github.com repository for ACM
This ACM enabled GKE cluster will have Config Sync poll my public gke-acm-kustomize-public repo for changes.
This repo uses the kustomize overlay system to generate deployments. If you need a walk-through of kustomize and its overlay system, see my previous article on kustomize. The repository has two base yaml deployments:
- reloader looks for configmap changes and does rolling restart of a deployment if a change event occurs
- nginx-index-html delivers a custom index.html page based on configmap content
From these bases, we generate the following kustomize overlay:
- nginx-index-with-reloader an nginx deployment serving a public page that restarts itself if the configmap changes
Private git repository requiring authentication
This entire section is not necessary if you are accessing a public git repository (like this article), BUT if the ACM git repo requires credentials then you will need to create a secret named ‘git-creds’ in the ‘config-management-system’ namespace.
Complete details on the use of ssh keys and personal access tokens for the major git providers is described in the official docs, but for our purposes here I will use an ssh key for a private github.com repository.
Create ssh key
git_id=$(git config user.email) echo "git_id = $git_id" # creates public private pair # /tmp/acm and /tmp/acm.pub ssh-keygen -t rsa -b 4096 -C "$git_id" -N '' -f /tmp/acm
Load private key into Kubernetes secret
kubectl create ns config-management-system kubectl create secret generic git-creds --namespace=config-management-system --from-file=ssh=/tmp/acm
Load public key into github deploy keys
The public side of the ssh pair needs to be added to the github private repository. After navigating to the private repository, select Settings>Deploy keys as shown below.
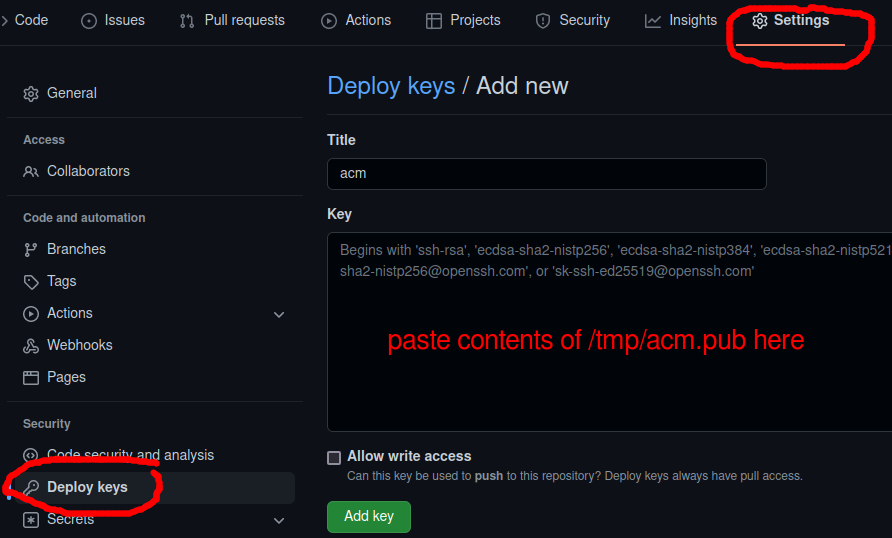
Use “acm” as the title and paste in the contents of “/tmp/acm.pub” into the textbox, then press “Add Key”. Now it has become a valid authentication method to this private repository via ssh.
Configure Cloud Sync using gcloud
As described in the documentation, we need to tailor a yaml file that describes our ConfigSync settings that can be applied via gcloud (not kubectl!).
# apply-spec.yaml
applySpecVersion: 1
spec:
configSync:
enabled: true
sourceFormat: unstructured
# if private repo using ssh key
#syncRepo: git@github.com:fabianlee/gke-acm-kustomize-private.git
#secretType: ssh
# if public repo with no auth
syncRepo: https://github.com/fabianlee/gke-acm-kustomize-public.git
secretType: none
syncBranch: main
# 300 seconds between polls
syncWait: 300
policyDir: overlays/nginx-index-with-reloader
preventDrift: false
Notice the policyDir attribute is set to the kustomize overlay directory ‘overlays/nginx-index-with-reloader‘.
You can validate that ACM is not configured for the cluster yet.
# nomos will report ACM is not installed yet $ nomos status Connecting to clusters... *gke_my-gkeproj1-10941_us-east1-b_std-prv-10-0-100-0 -------------------- NOT INSTALLED The ACM operator is neither installed in the "kube-system" namespace nor the "config-management-system" namespace # kubectl will not find root-sync object yet $ kubectl get rootsyncs.configsync.gke.io -n config-management-system root-sync -o yaml error: the server doesn't have a resource type "rootsyncs"
Run the ‘gcloud container hub’ command to apply the yaml configuration.
# view membership names, expect match with cluster name gcloud container hub memberships list # apply configuration gcloud beta container hub config-management apply --membership=$cluster_name --config=apply-spec.yaml --project=$project_id
The supporting objects will now begin to be created.
# details from yaml can now be found in this configmap $ kubectl describe configmap reconciler-manager-cm -n config-management-system # wait for deployments to become healthy $ kubectl get deployments -n config-management-system NAME READY UP-TO-DATE AVAILABLE AGE config-management-operator 1/1 1 1 7m1s reconciler-manager 1/1 1 1 6m50s root-reconciler 1/1 1 1 5m51s # wait for root-reconciler to be ready kubectl wait deployment -n config-management-system root-reconciler --for condition=Available=True # should not see errors in reconciler log kubectl logs deployment/root-reconciler -n config-management-system -c git-sync | tail -n10 # rootsync object now populated kubectl get rootsyncs.configsync.gke.io -n config-management-system root-sync -o yaml
Validate ACM management
The nomos utility will show status as ‘PENDING’ or ‘Unknown’ until reconciliation happens at which point the status will change to ‘Current’ as shown below.
$ nomos status
Connecting to clusters...
*gke_my-gkeproj1-10941_us-east1-b_std-prv-10-0-100-0
--------------------
:root-sync https://github.com/fabianlee/gke-acm-kustomize-public.git/overlays/nginx-index-with-reloader@main
SYNCED eb38685f2a2e735a920a774106eb8cd495cdd049
Managed resources:
NAMESPACE NAME STATUS SOURCEHASH
clusterrole.rbac.authorization.k8s.io/reloader-reloader-role Current eb38685
clusterrolebinding.rbac.authorization.k8s.io/reloader-reloader-role-binding Current eb38685
namespace/nginx-index-reloader Current eb38685
namespace/reloader Current eb38685
nginx-index-reloader configmap/nginx-cm Current eb38685
nginx-index-reloader deployment.apps/nginx-deployment Current eb38685
nginx-index-reloader service/nginx-service Current eb38685
reloader deployment.apps/reloader-reloader Current eb38685
reloader serviceaccount/reloader-reloader Current eb38685
After the ACM reconciliation and creation of the ‘reload’ component and customized nginx deployment, we now have two namespaces under ACM management.
# show namespaces controlled by ACM $ kubectl get ns -l app.kubernetes.io/managed-by=configmanagement.gke.io NAME STATUS AGE nginx-index-reloader Active 19m reloader Active 37m
And a curl from inside the customize NGINX deployment will show us the content of the custompub configmap from cm-index.html.
$ kubectl exec -it -n nginx-index-reloader deployment/nginx-deployment -- curl http://localhost <html><head></head> <body> <h1>nginx-index-html enhanced with reloader</h1> </body> </html>
Validate ACM change
With proof that ACM is now managing the NGINX overlay deployment, let’s take it a step further and prove that a push to the git repository will get reflected in the cluster.
In order to commit your own changes, you will need to first create a personal fork using the github.com web UI. And then be sure to reapply the apply-spec.yaml with your personal fork in the ‘syncRepo’ attribute.
# clone git repo and make change # create your own personal fork to make changes git clone https://github.com/fabianlee/gke-acm-kustomize-public.git cd gke-acm-kustomize-public # change into the overlays directory cd overlays/nginx-index-with-reloader/nginx-index # add 'testing123' to the delivered content sed -i 's/reloader/reloader testing123/' cm-index.html # commit and push change git commit -a -m "changed configmap with index.html content" git push # get latest commit hash latest_git_hash=$(git log --format=format:%H -n1) echo "latest_git_hash = $latest_git_hash" # view reconciler logs based on git hash kubectl logs deployment/root-reconciler -n config-management-system -c git-sync | grep f1dbb6bfe974cfc79b3dc2501afa106ed28e0865 # check for nomos status changing from "PENDING" to 'Current' nomos status # check content again, 'testing123' added to index.html $ kubectl exec -it -n nginx-index-reloader deployment/nginx-deployment -- curl http://localhost <html><head></head> <body> <h1>nginx-index-html enhanced with reloader testing123</h1> </body> </html>
REFERENCES
acm-workshop, walk through tutorial
google ref, ACM configuring only a subset of clusters
google ref, troubleshooting ACM
stakater/Reloader github project
github fabianlee, gke-acm-kustomize-public used for ACM
Johannes Glenn, ACM for GKE clusters
google ref, ACM enablement with Terraform
Mike Sparr, ArgoCD as git pipeline
google ref, configure k8s with kustomize
stakater Reloader, watches for changes in configmap/secrets and reloads
google ref, all supported fields for apply-spec.yaml
google ref, enable workload identity on GKE cluster
google ref, prereq for registering a cluster
google ref, registering cluster using workload identity as auth
Anchit Nishant, GKE and ACM walkthrough
NOTES
View rootstync config
kubectl -n config-management-system get rootsync root-sync -o=jsonpath="{.spec}" | jq .
Creating git-creds secret for git credentials with user and password/PAT
kubectl delete secret git-creds --namespace=config-management-system kubectl create secret generic git-creds --namespace=config-management-system --from-literal=username=mygituser --from-literal=token=myGitP4ss kubectl rollout restart deployment root-reconciler -n config-management-system kubectl get deployment -n config-management-system root-reconciler kubectl wait deployment -n config-management-system root-reconciler --for condition=Available=True --timeout=90s kubectl logs -f deployment/root-reconciler -n config-management-system -c git-sync
getting gsutil to use gcloud credentials [link]
# first, having IPv6 enabled can cause gsutil to hang, make sure /etc/sysctl.conf is loaded sudo sysctl -p # to pass on gcloud credentials gcloud config set pass_credentials_to_gsutil true # to use browser auth gsutil config -b
install and use github CLI tool [install, fork, deploy-key, rename, repo delete]
# install using apt curl -fsSL https://cli.github.com/packages/githubcli-archive-keyring.gpg | sudo dd of=/usr/share/keyrings/githubcli-archive-keyring.gpg echo "deb [arch=$(dpkg --print-architecture) signed-by=/usr/share/keyrings/githubcli-archive-keyring.gpg] https://cli.github.com/packages stable main" | sudo tee /etc/apt/sources.list.d/github-cli.list > /dev/null sudo apt update sudo apt install gh # create credentials for 'gh' gh auth login # create personal fork of another project gh repo fork https://github.com/macagua/example.java.helloworld gh repo fork git@github.com:macagua/example.java.helloworld.git cd example.java.helloworld/ git remote -v # create public private ssh keypair git_id=$(git config user.email) ssh-keygen -t rsa -b 4096 -C "$git_id" -N '' -f testkey # upload public side of ssh key to repo gh repo deploy-key add testkey.pub # rename repo, then local directory to match gh repo rename example.java.helloworld-private cd .. mv example.java.helloworld example.java.helloworld-private cd example.java.helloworld-private # delete key from repo gh repo deploy-key list key_id=(gh repo deploy-key list | cut -f1) gh repo deploy-key delete $key_id # delete repo, first give auth scope to do deletions gh auth refresh -h github.com -s delete_repo gh repo delete cd .. rm -fr example.java.helloworld-private
View all objects under ConfigSync control
kubectl api-resources | grep -E "configmanagement.gke.io|configsync.gke.io"
Stop ACM sync, docs link
OPERATOR_NAMESPACE=config-management-system kubectl scale -n $OPERATOR_NAMESPACE deployment config-management-operator --replicas=0 \ && kubectl wait -n $OPERATOR_NAMESPACE --for=delete pods -l k8s-app=config-management-operator \ && kubectl scale -n config-management-system deployment --replicas=0 --all \ && kubectl wait -n config-management-system --for=delete pods --all
Resume ACM sync, docs link
OPERATOR_NAMESPACE=config-management-system kubectl -n $OPERATOR_NAMESPACE scale deployment config-management-operator --replicas=1